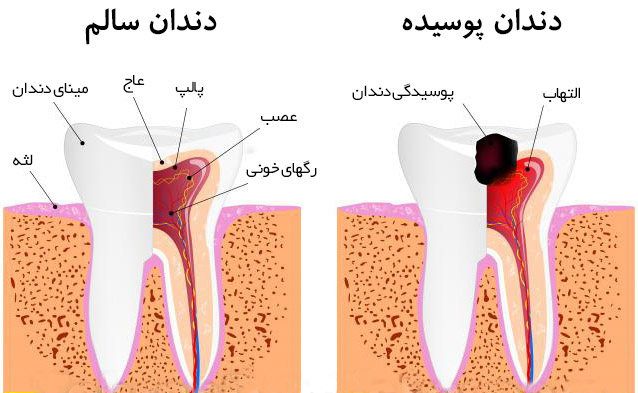
Tooth decay is the most common dental disease that affects people of all ages. Tooth decay is an infectious disease that begins with the activity of microbes on the surface of the tooth and progresses in its structure. Failure to take care in time can cause tooth loss. For decay to occur, sugary substances must be available to microbes to produce acid, which destroys the mineral structure. In fact, tooth decay is the destruction of hard tooth tissues.
The common areas of caries do not affect all tooth surfaces equally. Rather, some surfaces of the teeth are more prone to decay due to their special condition. These levels are:
Grooves on the occlusal surface: The occlusal surface of the posterior teeth has narrow and deep grooves that provide a suitable environment for the life and growth of microbes and the tooth decays from this place.
Interdental surfaces: This area cannot be cleaned due to the lack of penetration by the bristles of the toothbrush, so it is considered one of the areas prone to dental caries and periodontal disease.
Tooth cervical or the area where the gum connects to the tooth: the accumulation of microbes in this area usually causes gum disease in addition to causing decay.
Signs of dental caries:
When a tooth decays, it may have one or more of the following symptoms.
Discoloration of tooth enamel: the accumulation of microbes usually turns brown or black in the place of enamel decay.
Creating a cavity at the site of decay: the accumulation of microbes usually at the site of decay, sometimes a large amount of the tooth is lost, so that a person thinks that his tooth is broken.
Tooth sensitivity or pain: when eating cold, hot, sour and sweet foods and when the teeth are pressed together.
Although dental caries are detected by clinical examinations, interdental caries and caries under existing restorations cannot be diagnosed with the help of clinical examinations alone, and radiography is necessary to identify the presence and extent of such caries.



