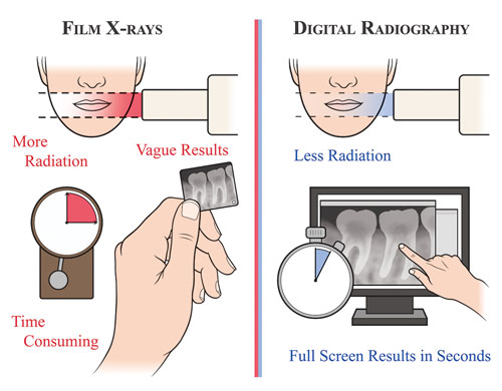
In recent years, a special type of simple radiography has become popular, which is called digital radiography. The difference between this method and the traditional method is the image receiver used. This is the difference between new digital cameras and old cameras. Old photographic cameras recorded the image on a film and that film had to be exposed in the laboratory and then printed on paper, but in digital cameras, the image instead of the film is projected onto a light-sensitive electronic screen, which converts the optical information of the image. to electrical signals.
In digital radiography, instead of radiology film, the image receiver contains an electronic screen that does the same thing. The impact of X-rays that have passed through the patient's body on the electronic screen stimulates the semiconductors on it. These semiconductors generate electric current intensity according to the intensity of the rays that hit them. The information of these electrical signals is processed by the computer and can be seen on the monitor. Of course, the images obtained from this type of radiography can also be printed on film.
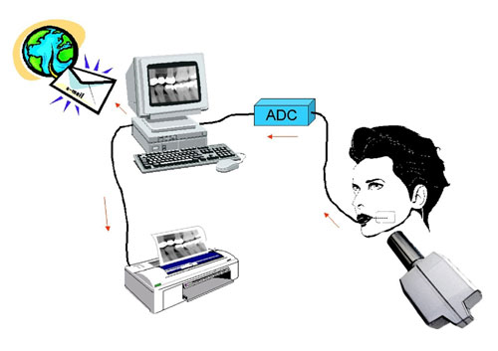
Advantages of digital radiography
• High speed of image preparation
• Reducing costs to remove the film
• The ability to archive images with greater ease and the ability to copy any number of videos without spending extra money
• The ability to send images through electronic channels or through the Internet
• The physician's ability to access the radiographic image as soon as it is prepared and at another point • Better quality of images
• The possibility of modifying the image (such as enlarging and reducing, brightening and darkening, changing the contrast of the image, marking on the image).
Disadvantages of digital radiology :
1- The cost of setting up digital radiography for dentists is very high
2- Setting up digital radiography in dental practices requires special training that must be periodically updated so that a person is aware of new technologies that are quickly becoming outdated.
3- PSP sensors are thinner than film plates and this exposes them to bending and in most cases they need to be replaced.
Types of digital radiography methods:
In digital X-ray imaging equipment, various techniques are used in order to reduce the dose of radiation and increase the quality of images, as well as eliminate the need for film in each exposure. In general, digital X-ray imaging equipment can be divided into the following two categories:
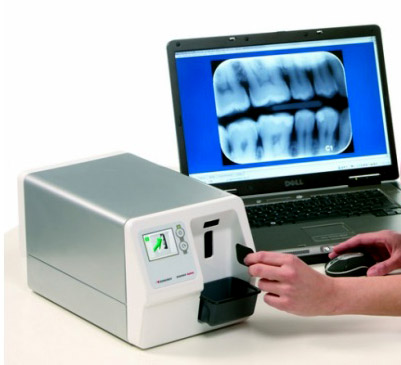

Photostimulating phosphor technology (CR):
The way CR devices work is that instead of film, a light-sensitive phosphor screen is used for imaging. By applying exposure, different points of the screen receive energy in proportion to the energy of the absorbed photons. By placing the phosphor plate in the scanner and irradiating the laser beam to each of these points and traveling the length of the lines by the laser, the absorbed energy of the particles is emitted as light, which is received by a special lamp (photo-multiplier tube) and the resulting signal enters the analog-to-digital converter and a digital image is created. This scanner directly refers the image file to the relevant computer and the image can be viewed on the monitor.
Solid state technology (DR):
⦁ charge-coupled device (CCD)
⦁ complementary metal oxide semiconductors (CMOS)
⦁ Flat panel
The newest DR technology is flat panels. Since in these flat panels, the energy of X-ray photons passes through the patient's body, it is directly converted into electric current (there is no need to convert X-rays into light), they are called direct digital detectors. The outer layer of these panels consists of a high voltage electrode (with a potential difference of about 5000 volts) in order to increase the rate of absorption of X-ray photons energy on the selenium surface and cause the generated charges to be attracted to the electrodes. These radiation detector plates consists of millions of pixels (millions of small capacitors and transistors connected to it).