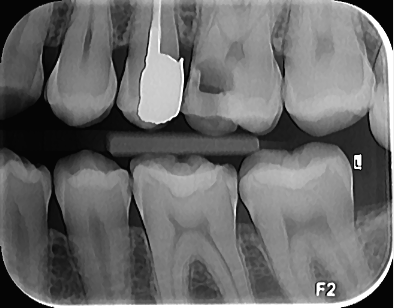
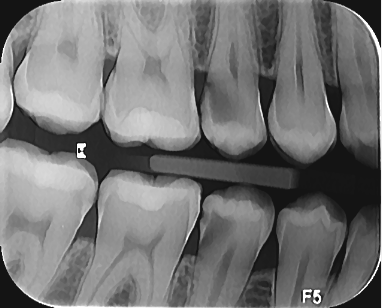
Also, this radiograph can reveal secondary caries under restorations that may not be detected in periapical views. Also, this radiography is effective and useful for evaluating the state of the interdental bone and detecting mass deposits in the interdental areas. Since the diagnosis of interdental caries through clinical examinations alone is not reliable, it is necessary for patients to periodically undergo bite wing radiographic examinations to control dental caries. The length of periodic intervals between the preparation of radiographs varies significantly due to the different conditions of the patients. For most patients with good physical health and good oral and dental hygiene, a time interval of 24 to 36 months is recommended, and for patients whose history and clinical examination If it shows relatively high dental caries, it is recommended to take radiographs at shorter intervals (6 to 18 months). Of course, it should be noted that these intervals are shorter in children. In children with good oral hygiene and without clinical caries, every 12 to 24 months, and in children with a high risk of caries every 6 to 12 months, preparation of bitewing radiographs is recommended in order to identify interdental caries.